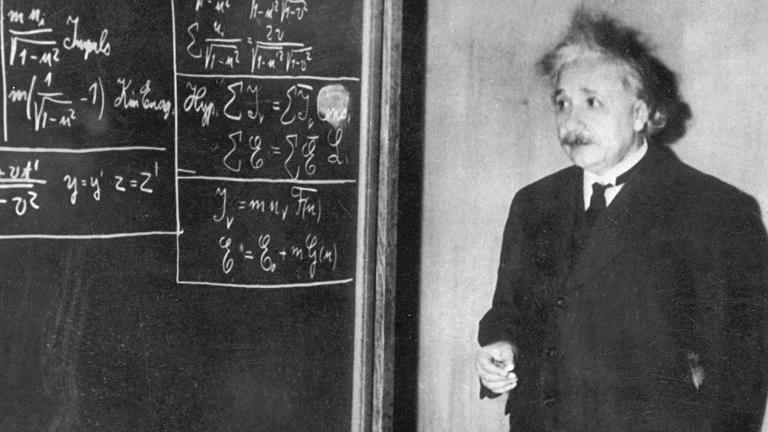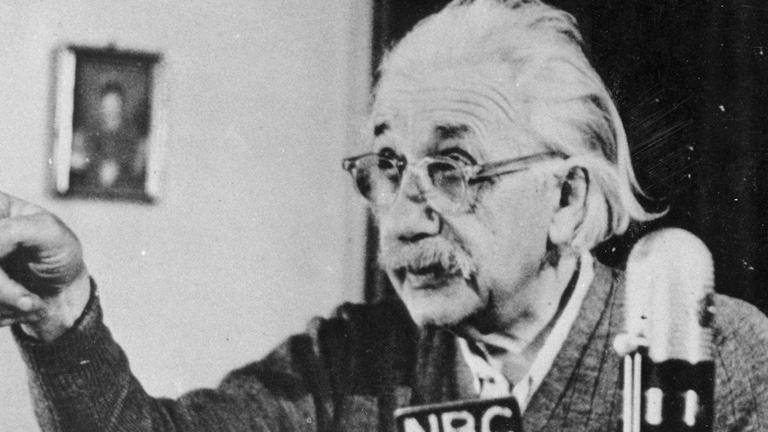Inventor Nikola Tesla contributed to the development of the alternating-current electrical system that's widely used today and discovered the rotating magnetic field (the basis of most AC machinery).
Likry
Wednesday, November 25, 2015
Tesla Biography - part 1
NIKOLA TESLA
THE GENIUS WHO LIT THE WORLD

Nikola Tesla symbolizes a unifying force and inspiration for all nations in the name of peace and science. He was a true visionary far ahead of his contemporaries in the field of scientific development. New York State and many other states in the USA proclaimed July 10, Tesla’s birthday- Nikola Tesla Day.
Many United States Congressmen gave speeches in the House of Representatives on July 10, 1990 celebrating the 134th anniversary of scientist-inventor Nikola Tesla. Senator Levine from Michigan spoke in the US Senate on the same occasion.
The street sign “Nikola Tesla Corner” was recently placed on the corner of the 40th Street and 6th Avenue in Manhattan. There is a large photo of Tesla in the Statue of Liberty Museum. The Liberty Science Center in Jersey City, New Jersey has a daily science demonstration of the Tesla Coil creating a million volts of electricity before the spectators eyes. Many books were written about Tesla :Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla by John J. O’Neill and Margaret Cheney’s book Tesla: Man out of Time has contributed significantly to his fame. A documentary film Nikola Tesla, The Genius Who Lit the World, produced by the Tesla Memorial Society and the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade,The Secret of Nikola Tesla (Orson Welles), BBC Film Masters of the Ionosphere are other tributes to the great genius.
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856 in Smiljan, Lika, which was then part of the Austo-Hungarian Empire, region of Croatia. His father, Milutin Tesla was a Serbian Orthodox Priest and his mother Djuka Mandic was an inventor in her own right of household appliances. Tesla studied at the Realschule, Karlstadt in 1873, the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria and the University of Prague. At first, he intended to specialize in physics and mathematics, but soon he became fascinated with electricity. He began his career as an electrical engineer with a telephone company in Budapest in 1881. It was there, as Tesla was walking with a friend through the city park that the elusive solution to the rotating magnetic field flashed through his mind. With a stick, he drew a diagram in the sand explaining to his friend the principle of the induction motor. Before going to America, Tesla joined Continental Edison Company in Paris where he designed dynamos. While in Strassbourg in 1883, he privately built a prototype of the induction motor and ran it successfully. Unable to interest anyone in Europe in promoting this radical device, Tesla accepted an offer to work for Thomas Edison in New York. His childhood dream was to come to America to harness the power of Niagara Falls.
Young Nikola Tesla came to the United States in 1884 with an introduction letter from Charles Batchelor to Thomas Edison: “I know two great men,” wrote Batchelor, “one is you and the other is this young man.” Tesla spent the next 59 years of his productive life living in New York. Tesla set about improving Edison’s line of dynamos while working in Edison’s lab in New Jersey. It was here that his divergence of opinion with Edison over direct current versus alternating current began. This disagreement climaxed in the war of the currents as Edison fought a losing battle to protect his investment in direct current equipment and facilities.
Tesla pointed out the inefficiency of Edison’s direct current electrical powerhouses that have been build up and down the Atlantic seaboard. The secret, he felt, lay in the use of alternating current ,because to him all energies were cyclic. Why not build generators that would send electrical energy along distribution lines first one way, than another, in multiple waves using the polyphase principle?
Edison’s lamps were weak and inefficient when supplied by direct current. This system had a severe disadvantage in that it could not be transported more than two miles due to its inability to step up to high voltage levels necessary for long distance transmission. Consequently, a direct current power station was required at two mile intervals.
Direct current flows continuously in one direction; alternating current changes direction 50 or 60 times per second and can be stepped up to vary high voltage levels, minimizing power loss across great distances. The future belongs to alternating current.
Nikola Tesla developed polyphase alternating current system of generators, motors and transformers and held 40 basic U.S. patents on the system, which George Westinghouse bought, determined to supply America with the Tesla system. Edison did not want to lose his DC empire, and a bitter war ensued. This was the war of the currents between AC and DC. Tesla -Westinghouse ultimately emerged the victor because AC was a superior technology. It was a war won for the progress of both America and the world.
Tesla introduced his motors and electrical systems in a classic paper, “A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers” which he delivered before the American Institute of Electrical Engineers in 1888. One of the most impressed was the industrialist and inventor George Westinghouse. One day he visited Tesla’s laboratory and was amazed at what he saw. Tesla had constructed a model polyphase system consisting of an alternating current dynamo, step-up and step-down transformers and A.C. motor at the other end. The perfect partnership between Tesla and Westinghouse for the nationwide use of electricity in America had begun.
In February 1882, Tesla discovered the rotating magnetic field, a fundamental principle in physics and the basis of nearly all devices that use alternating current. Tesla brilliantly adapted the principle of rotating magnetic field for the construction of alternating current induction motor and the polyphase system for the generation, transmission, distribution and use of electrical power.
Tesla’s A.C. induction motor is widely used throughout the world in industry
and household appliances. It started the industrial revolution at the turn of the
century. Electricity today is generated transmitted and converted to mechanical
power by means of his inventions. Tesla’s greatest achievement is his polyphase
alternating current system, which is today lighting the entire globe.
Tesla astonished the world by demonstrating. the wonders of alternating current electricity at the World Columbian Exposition in Chicago in 1893. Alternating current became standard power in the 20th Century. This accomplishment changed the world. He designed the first hydroelectric powerplant in Niagara Falls in 1895, which was the final victory of alternating current. The achievement was covered widely in the world press, and Tesla was praised as a hero world wide. King Nikola of Montenegro conferred upon him the Order of Danilo.
Tesla was a pioneer in many fields. The Tesla coil, which he invented in 1891, is widely used today in radio and television sets and other electronic equipment. That year also marked the date of Tesla's United States citizenship. His alternating current induction motor is considered one of the ten greatest discoveries of all time. Among his discoveries are the fluorescent light , laser beam, wireless communications, wireless transmission of electrical energy, remote control, robotics, Tesla’s turbines and vertical take off aircraft. Tesla is the father of the radio and the modern electrical transmissions systems. He registered over 700 patents worldwide. His vision included exploration of solar energy and the power of the sea. He foresaw interplanetary communications and satellites.
The Century Magazine published Tesla's principles of telegraphy without wires, popularizing scientific lectures given before Franklin Institute in February 1893.
The Electrical Review in 1896 published X-rays of a man, made by Tesla, with X-ray tubes of his own design. They appeared at the same time as when Roentgen announced his discovery of X-rays. Tesla never attempted to proclaim priority. Roentgen congratulated Tesla on his sophisticated X-ray pictures, and Tesla even wrote Roentgen's name on one of his films. He experimented with shadowgraphs similar to those that later were to be used by Wilhelm Rontgen when he discovered X-rays in 1895. Tesla's countless experiments included work on a carbon button lamp, on the power of electrical resonance, and on various types of lightning. Tesla invented the special vacuum tube which emitted light to be used in photography.
The breadth of his inventions is demonstrated by his patents for a bladeless steam turbine based on a spiral flow principle. Tesla also patented a pump design to operate at extremely high temperature.
Nikola Tesla patented the basic system of radio in 1896. His published schematic diagrams describing all the basic elements of the radio transmitter which was later used by Marconi.
In 1896 Tesla constructed an instrument to receive radio waves. He experimented with this device and transmitted radio waves from his laboratory on South 5th Avenue. to the Gerlach Hotel at 27th Street in Manhattan. The device had a magnet which gave off intense magnetic fields up to 20,000 lines per centimeter. The radio device clearly establishes his piority in the discovery of radio.
The shipboard quench-spark transmitter produced by the Lowenstein Radio Company and licensed under Nikola Tesla Company patents, was installed on the U.S. Naval vessels prior to World War I.
In December 1901, Marconi established wireless communication between Britain and the Newfoundland, Canada, earning him the Nobel prize in 1909. But much of Marconi's work was not original. In 1864, James Maxwell theorized electromagnetic waves. In 1887, Heinrich Hertz proved Maxwell's theories. Later, Sir Oliver Logde extended the Hertz prototype system. The Brandley coherer increased the distance messages could be transmitted. The coherer was perfected by Marconi.
However, the heart of radio transmission is based upon four tuned circuits for transmitting and receiving. It is Tesla's original concept demonstrated in his famous lecture at the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia in 1893. The four circuits, used in two pairs, are still a fundamental part of all radio and television equipment.
The United States Supreme Court, in 1943 held Marconi's most important patent invalid, recognizing Tesla's more significant contribution as the inventor of radio technology.
Tesla built an experimental station in Colorado Springs, Colorado in 1899, to experiment with high voltage, high frequency electricity and other phenomena.
When the Colorado Springs Tesla Coil magnifying transmitter was energized, it created sparks 30 feet long. From the outside antenna, these sparks could be seen from a distance of ten miles. From this laboratory, Tesla generated and sent out wireless waves which mediated energy, without wires for miles.
In Colorado Springs, where he stayed from May 1899 until 1900, Tesla made what he regarded as his most important discovery-- terrestrial stationary waves. By this discovery he proved that the Earth could be used as a conductor and would be as responsive as a tuning fork to electrical vibrations of a certain frequency. He also lighted 200 lamps without wires from a distance of 25 miles( 40 kilometers) and created man-made lightning. At one time he was certain he had received signals from another planet in his Colorado laboratory, a claim that was met with disbelief in some scientific journals.
The old Waldorf Astoria was the residence of Nikola Tesla for many years. He lived there when he was at the height of financial and intellectual power. Tesla organized elaborate dinners, inviting famous people who later witnessed spectacular electrical experiments in his laboratory.
Financially supported by J. Pierpont Morgan, Tesla built the Wardenclyffe laboratory and its famous transmitting tower in Shoreham, Long Island between 1901 and 1905. This huge landmark was 187 feet high, capped by a 68-foot copper dome which housed the magnifying transmitter. It was planned to be the first broadcast system, transmitting both signals and power without wires to any point on the globe. The huge magnifying transmitter, discharging high frequency electricity, would turn the earth into a gigantic dynamo which would project its electricity in unlimited amounts anywhere in the world.
Tesla's concept of wireless electricity was used to power ocean liners, destroy warships, run industry and transportation and send communications instantaneously all over the globe. To stimulate the public's imagination, Tesla suggested that this wireless power could even be used for interplanetary communication. If Tesla were confident to reach Mars, how much less difficult to reach Paris. Many newspapers and periodicals interviewed Tesla and described his new system for supplying wireless power to run all of the earth's industry.
Because of a dispute between Morgan and Tesla as to the final use of the tower. Morgan withdrew his funds. The financier's classic comment was, "If anyone can draw on the power, where do we put the meter?"
The erected, but incomplete tower was demolished in 1917 for wartime security reasons. The site where the Wardenclyffe tower stood still exists with its 100 feet deep foundation still intact. Tesla's laboratory designed by Stanford White in 1901 is today still in good condition and is graced with a bicentennial plaque.
Tesla lectured to the scientific community on his inventions in New York, Philadelphia and St. Louis and before scientific organizations in both England and France in 1892. Tesla’s lectures and writings of the 1890s aroused wide admiration among contemporaries popularized his inventions and inspired untold numbers of younger men to enter the new field of radio and electrical science.
Nikola Tesla was one of the most celebrated personalities in the American press, in this century. According to Life Magazine's special issue of September, 1997, Tesla is among the 100 most famous people of the last 1,000 years. He is one of the great men who divert the stream of human history. Tesla's celebrity was in its height at the turn of the century. His discoveries, inventions and vision had widespread acceptance by the public, the scientific community and American press. Tesla's discoveries had extensive coverage in the scientific journals, the daily and weekly press as well as in the foremost literary and intellectual publications of the day. He was the Super Star.
Tesla wrote many autobiographical articles for the prominent journal Electrical Experimenter, collected in the book, My Inventions. Tesla was gifted with intense powers of visualization and exceptional memory from early youth on. He was able to fully construct, develop and perfect his inventions completely in his mind before committing them to paper.
According to Hugo Gernsback, Tesla was possessed of a striking physical appearance over six feet tall with deep set eyes and a stately manner. His impressions of Tesla, were of a man endowed with remarkable physical and mental freshness, ready to surprise the world with more and more inventions as he grew older. A lifelong bachelor he led a somewhat isolated existence, devoting his full energies to science.
In 1894, he was given honorary doctoral degrees by Columbia and Yale University and the Elliot Cresson medal by the Franklin Institute. In 1934, the city of Philadelphia awarded him the John Scott medal for his polyphase power system. He was an honorary member of the National Electric Light Association and a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. On one occasion, he turned down an invitation from Kaiser Wilhelm II to come to Germany to demonstrate his experiments and to receive a high decoration.
In 1915, a New York Times article announced that Tesla and Edison were to share the Nobel Prize for physics. Oddly, neither man received the prize, the reason being unclear. It was rumored that Tesla refused the prize because he would not share with Edison, and because Marconi had already received his.

(Tesla's friend Mark Twain, famous American writer)
On his 75th birthday in 1931, the inventor appeared on the cover of Time Magazine. On this occasion, Tesla received congratulatory letters from more than 70 pioneers in science and engineering including Albert Einstein. These letters were mounted and presented to Tesla in the form of a testimonial volume.

Tesla died on January 7th, 1943 in the Hotel New Yorker, where he had lived for the last ten years of his life. Room 3327 on the 33rd floor is the two-room suites he occupied.
A state funeral was held at St. John the Divine Cathedral in New York City. Telegrams of condolence were received from many notables, including the first lady Eleanor Roosevelt and Vice President Wallace. Over 2000 people attended, including several Nobel Laureates. He was cremated in Ardsley on the Hudson, New York. His ashes were interned in a golden sphere, Tesla’s favorite shape, on permanent display at the Tesla Museum in Belgrade along with his death mask.
In his speech presenting Tesla with the Edison medal, Vice President Behrend of the Institute of Electrical Engineers eloquently expressed the following: "Were we to seize and eliminate from our industrial world the result of Mr. Tesla's work, the wheels of industry would cease to turn, our electric cars and trains would stop, our towns would be dark and our mills would be idle and dead. His name marks an epoch in the advance of electrical science." Mr. Behrend ended his speech with a paraphrase of Pope's lines on Newton: "Nature and nature's laws lay hid by night. God said 'Let Tesla be' and all was light."
“The world will wait a long time for Nikola Tesla’s equal in
achievement and imagination.” E. ARMSTRONG
Nikola Tesla’s Awards and Recognition
In 1917, Tesla was awarded the Edison Medal, the most coveted electrical prize in the United States.
Nikola Tesla’s name has been honored with an International Unit of Magnetic Flux Density called “Tesla."
The United States Postal Service honored Tesla with a commemorative stamp in 1983.
Tesla was inducted into the Inventor’s Hall of Fame in 1975.
The Nikola Tesla Award is one of the most distinguished honors presented by the Institute of Electrical Engineers. The award has been given annually since 1976.
The Nikola Tesla Statue is located on Goat Island to honor the man whose inventions were incorporated into the Niagara Falls Power Station in 1895. Tesla is known as the inventor of polyphase alternating current.
The Nikola Tesla Corner Sign, located at the intersection of 40th Street and 6th Avenue in Manhattan, is a constant reminder to all New Yorkers of the greatness of this genius.
Albert Einstein Biography
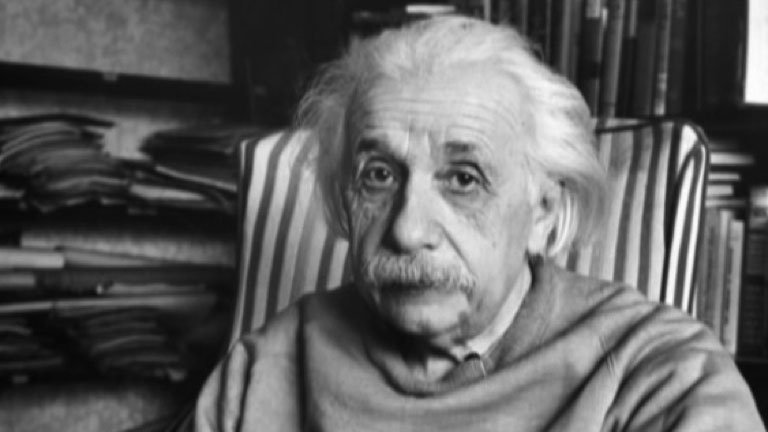
Albert Einstein was a German-born physicist who developed the general theory of relativity, among other feats. He is considered the most influential physicist of the 20th century.
Born in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany in 1879, Albert Einstein had a passion for inquiry that eventually led him to develop the special and general theories of relativity. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize for physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect and immigrated to the U.S. in the following decade after being targeted by the Nazis. Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20th century, with his work also having a major impact on the development of atomic energy. With a focus on unified field theory during his later years, Einstein died on April 18, 1955, in Princeton, New Jersey.
Resident of Switzerland
Marriage and Family
Miracle Year
Relativity and Nobel Prize
Move to U.S. and Atomic Energy
Global and Domestic Activism
Final Years and Legacy
Videos

25
GALLERY
Born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany, Albert Einstein grew up in a secular Jewish family. His father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer who with his brother founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a Munich-based company that manufactured electrical equipment. His mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. Einstein had one sister, Maja, born two years after him.
Einstein attended elementary school at the Luitpold Gymnasium in Munich. However, he felt alienated there and struggled with the institution's rigid pedagogical style. He also had what were considered to be speech challenges, though he developed a passion for classical music and playing the violin that would stay with him into his later years. Most significantly, Einstein's youth was marked by deep inquisitiveness and inquiry.
Towards the end of the 1880s, Max Talmud, a Polish medical student who sometimes dined with the Einstein family, became an informal tutor to young Albert. Talmud had introduced his pupil to a children’s science text that inspired Einstein to dream about the nature of light. Thus, during his teens, Einstein penned what would be seen as his first major paper, "The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields."
Hermann Einstein relocated the family to Milan, Italy, in the mid-1890s after his business lost out on a major contract. Albert was left at a relative's boarding house in Munich to complete his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Faced with military duty when he turned of age, Albert allegedly withdrew from classes, using a doctor’s note to excuse himself and claim nervous exhaustion. With their son rejoining them in Italy, his parents understood Einstein's perspective but were concerned about his future prospects as a school dropout and draft dodger.
Einstein was eventually able to gain admission into the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich, specifically due to his superb mathematics and physics scores on the entrance exam. He was still required to complete his pre-university education first, and thus attended a high school in Aarau, Switzerland helmed by Jost Winteler. Einstein lived with the schoolmaster's family and fell in love with Wintelers' daughter, Marie. Einstein later renounced his German citizenship and became a Swiss citizen at the dawn of the new century.
While attending school in Zurich, Einstein developed lasting friendships and alliances, also meeting his future wife, Mileva Maric, a Serbian physics student.
After graduating from Polytechnic, Einstein faced major challenges in terms of finding academic positions, having alienated some professors over not attending class more regularly in lieu of studying independently. Meanwhile, Einstein continued to grow closer to Maric, but his parents were strongly against the relationship due her ethnic background. Nonetheless, Einstein continued to see her, with the two developing a correspondence via letters in which he expressed many of his scientific ideas. In 1902 the couple had a daughter, Lieserl, who might have been later raised by Maric's relatives or given up for adoption. Her ultimate fate and whereabouts remain a mystery.
Einstein eventually found steady work in 1902 after receiving a referral for a clerk position in a Swiss patent office. Einstein’s father passed away shortly thereafter, and the young scientist married Milena Maric on Jan. 6, 1903. The couple went on to have two sons, Hans and Eduard.
The marriage would not be a happy one, however, with the two divorcing in 1919 and Maric having an emotional breakdown in connection to the split. Einstein, as part of a settlement, agreed to give Maric any funds he might receive from possibly winning the Nobel Prize in the future. He had also begun an affair some time earlier with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal, whom Einstein wed during the same year of his divorce. He would continue to see other women throughout his second marriage, which ended with Löwenthals death in 1936.
While working at the patent office, Einstein had the time to further ideas that had taken hold during his studies at Polytechnic and thus cemented his theorems on what would be known as the principle of relativity.
In 1905—seen by many as a "miracle year" for the theorist—Einstein had four papers published in the Annalen der Physik, one of the best known physics journals of the era. The four papers focused on the photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, the special theory of relativity (the most widely circulated of the write-ups) and the matter/energy relationship, thus taking physics in an electrifying new direction. In his fourth paper, Einstein came up with the equation E=mc2, suggesting that tiny particles of matter could be converted into huge amounts of energy, foreshadowing the development of atomic power.
Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein, who thus became a star of the lecture circuit and academia, taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics from 1913 to 1933.
In November, 1915, Einstein completed the general theory of relativity, which he considered the culmination of his life research. He was convinced of the merits of general relativity because it allowed for a more accurate prediction of planetary orbits around the sun, which fell short in Isaac Newton’s theory, and for a more expansive, nuanced explanation of how gravitational forces worked. Einstein's assertions were affirmed via observations and measurements by British astronomers Sir Frank Dyson and Sir Arthur Eddington during the 1919 solar eclipse, and thus a global science icon was born.
In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize for Physics though he wasn't actually given the award until the following year due to a bureaucratic ruling. Because his ideas on relativity were still considered questionable, he received the prize for his explanation of the photoelectric effect though Einstein still opted to speak about relativity during his acceptance speech.
In the development of his general theory, Einstein had held on to the belief that the universe was a fixed, static entity, aka a "cosmological constant," though his later theories directly contradicted this idea and asserted that the universe could be in a state of flux. Astronomer Edwin Hubble deduced that we indeed inhabit an expanding universe, with the two scientists meeting at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles in 1930.
While Einstein was travelling and speaking internationally, the Nazis, led byAdolf Hitler, were gaining prominence with violent propaganda and vitriol in an impoverished post-WWI Germany. The party influenced other scientists to label Einstein's work "Jewish physics." Jewish citizens were barred from university work and other official jobs, and Einstein himself was targeted to be killed.
In 1933, Einstein took on a position at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, New Jersey and never went back to his native land. It was here that he would spend the rest of his life working on a unified field theory—an all-embracing paradigm meant to unify the varied laws of physics. Other European scientists also left regions threatened by Germany and immigrated to the states, with there being concern over Nazi strategies to create an atomic weapon.
In 1939, Einstein and fellow physicist Leo Szilard wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt to alert him of the possibility of a Nazi bomb and to galvanize the United States to create its own nuclear weapons. The U.S. would eventually initiate the Manhattan Project, though Einstein would not take direct part in its implementation due to his pacifist and socialist affiliations. Einstein was also the recipient of much scrutiny and major distrust from FBI director J. Edgar Hoover.
Not long after he began his career at Princeton, Einstein expressed an appreciation for American "meritocracy" and the opportunities people had for free thought, a stark contrast to his own experiences coming of age. In 1935, Einstein was granted permanent residency in his adopted country and became an American citizen a few years later. During WWII, he worked on Navy-based weapons systems and made big monetary donations to the military by auctioning off manuscripts worth millions.
After learning of the 1945 bombing of Hiroshima, Japan, Einstein became a major player in efforts to curtail usage of the a-bomb. The following year he and Szilard founded the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists, and in 1947, via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly, Einstein espoused working with the United Nations to maintain nuclear weapons as a deterrent to conflict.
Around this time, Einstein also became a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People, seeing the parallels between the treatment of Jews in Germany and African Americans in the United States. He corresponded with scholar/activist W.E.B. Du Bois as well as performing artist Paul Robeson and campaigned for civil rights, calling racism a "disease" in a 1946 Lincoln University speech.
After the war, Einstein continued to work on his unified field theory and key aspects of the theory of general relativity, such as wormholes, the possibility of time travel, the existence of black holes and the creation of the universe. However, he became increasingly isolated from the rest of the physics community, whose eyes were set on quantum theory. In the last decade of his life, Einstein, who had always seen himself as a loner, withdrew even further from any sort of spotlight, preferring to stay close to Princeton and immerse himself in processing ideas with colleagues.
On April 17, 1955, while working on a speech to honor Israel's seventh anniversary, Einstein suffered an abdominal aortic aneurysm. He was taken to the University Medical Center at Princeton for treatment but refused surgery, believing that he had lived his life and was content to accept his fate. "I want to go when I want," he stated at the time. "It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly." Einstein died at the university medical center early the next morning—April 18, 1955—at the age of 76.
During the autopsy, Thomas Stoltz Harvey removed Einstein's brain, reportedly without the permission of his family, for preservation and future study by doctors of neuroscience. Einstein's remains were cremated and his ashes were scattered in an undisclosed location, following his wishes. After decades of study, Einstein's brain is now located at the Princeton University Medical Center. A veritable mountain of books have been written on the iconic thinker's life, including Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson and Einstein: A Biography by Jürgen Neffe, both from 2007. Einstein's own words are presented in the collection The World as I See It.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)